GBFS — More Than Just Slag
Granulated Blast Furnace Slag (GBFS)
More Than Just Slag — A Reliable Material for Modern Construction
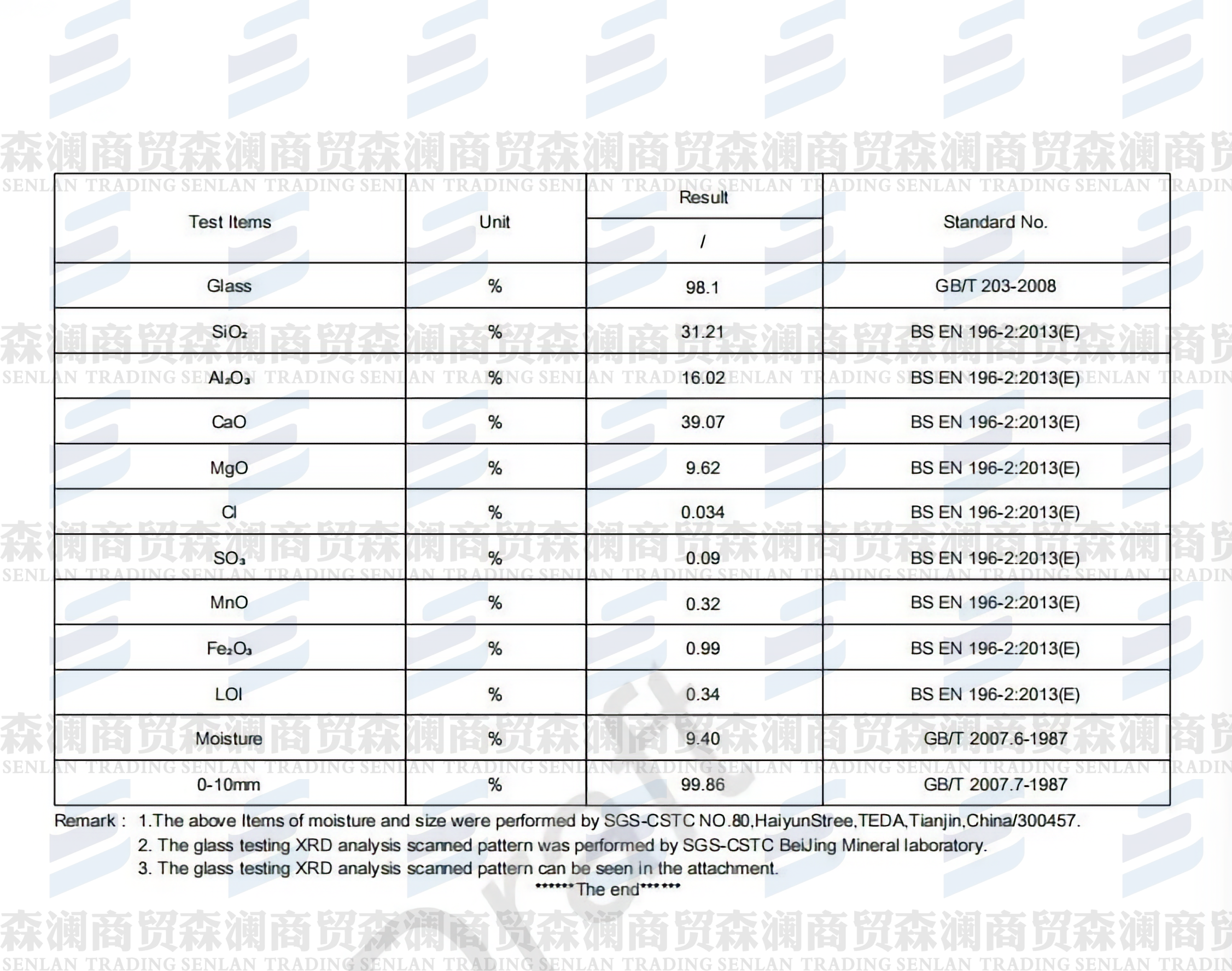
Granulated Blast Furnace Slag (GBFS) is primarily composed of reactive silicate compounds and is widely used as a construction material raw input and industrial auxiliary material. As a by-product of the ironmaking process, GBFS enables efficient resource recycling while delivering strong performance in building and infrastructure applications.
Core Chemical Composition
The main constituents of GBFS are dicalcium silicate (C₂S) and tricalcium silicate (C₃S), supported by tricalcium aluminate (C₃A) and tetracalcium aluminoferrite (C₄AF). These silicate and aluminosilicate compounds form the foundation of GBFS’s performance characteristics.
Secondary components include calcium oxide (CaO), silicon dioxide (SiO₂), aluminum oxide (Al₂O₃), and magnesium oxide (MgO). Exact proportions may vary slightly depending on iron ore and fuel sources used during production.
Performance · Versatility · Sustainability
〰️
Performance · Versatility · Sustainability 〰️
Key Application Value
• Construction Materials Applications
When finely ground, GBFS can be used to produce slag cement, significantly improving long-term strength, impermeability, and corrosion resistance. As a concrete admixture, it enhances workability, reduces heat of hydration, and improves overall construction performance and structural durability.
• Diversified Industrial Applications
GBFS can be further processed into slag powder (a high-performance construction additive) or mineral wool for thermal insulation. It is also suitable for road base filling, brick manufacturing, and as a supplementary raw material in glass-ceramic production.